Sahil Rajput
About Classes and Fun
Understanding Classes in JavaScript
JavaScript Classes - ECMAScript 2015 @ w3schools.com
Undeclared Variables Notify - Using ESLint
Example - Object, Array Object
const saf = () => [10,20,30]
const [p,q,r] = saf()
Read here - Function call and Function Reference@StackOverflow •Do you need the function to run now?
Than add the () to execute it
•Do you need to function to be referenced so it is called later?
Do not add the ().
•Do you want to pass the values and wants it to be executed later. Pass the values and get it referenced via the function.
like, either () => ( mamosa(23) ) or () => { mamosa(23) }
••> Also, here setTimeout() function expects 1st parameter as function reference and second parameter as time in milliseconds. i.e., setTimeout(function-reference, time-in-milliseconds).
The function passed as the first parameter to the setTimeout function is invoked one second after calling the setTimeout function. So what we refer to function reference is -
setTimeout(
function rafell(){setCounter(counter + 1)}
,
1000
)
or
setTimeout(
function (){setCounter(counter + 1)}
,
1000
)
or
setTimeout(
() => {setCounter(counter + 1)}
,
1000
)
or
setTimeout(
() => (setCounter(counter + 1))
,
1000
)
So, these were all the possible cases for the function reference.
Important Link for - call by value or reference - examples@StackOverflow
const App = (props) => {
const [ counter, setCounter ] = useState(0)
const handleClick = () => {
console.log('clicked')
}
return (
<div>
<div>{counter}</div>
<button onClick=handleClick> // onClick needs a "reference to function"(or function reference), not a "call to function"(or function call);;ALSO a fuction call would be like "handleClick()"
plus
</button>
</div>
)
and with the change to call by reference.
const App = (props) => {
const [ counter, setCounter ] = useState(0)
const handleClick = () => {
console.log('clicked')
}
return (
<div>
<div>{counter}</div>
<button onClick={() => handleClick()}> // THIS LINE even now works perfectly.
plus
</button>
</div>
)
Below example breaks.
const App = (props) => {
const [ counter, setCounter ] = useState(0)
const handleClick = () => {
console.log('clicked')
}
return (
<div>
<div>{counter}</div>
<button onClick={() => handleClick}> // THIS LINE now a fuction body which contains a "function reference" and thus, the onClick will not execute the handleClick() function.
plus
</button>
</div>
)
a function call can be a function reference - i.e., const setToValue = (value) => () => setCounter(value)
Here, setToValue(0) or setToValue(1) is a function call in itself but actually a function reference when the evaluation occurs.
• Double arrow functions can be thought of as functions that have to be called twice in order to get the final result.
• This way of utilizing functions that return functions is effectively the same thing as currying in functional programming. The term currying does not originate from functional programming, rather the term is deeply rooted in mathematics.
Double Arrow (My Lang): Function call to a function returning another function which returns a function call. ;)
currying
tu = (t) => () => () => () => console.log('hulaaa',t)
tu('sa')()()()
***
The example you are looking for:
tu = (t) => () => () => () => t()
tu(()=>console.log('sahil'))()()()
https://wesbos.com - Good LINK - tutor - JS react teacher
Setting Language mode to “JavaScript React”.I would feel the below is the easiest way of formatting the code
- Click on the bottom right on VS Code Editor where it says Javascript.
- You will see an option to Select the language Mode, here you can search for JavaScriptReact and select. That’s it. This should solve your problem.
Comments in JSX -
{/* A JSX comment */}
OR
{/*
Multi
line
comment
*/}
NO nee - extra worries - [46 k, downloads]React Syntax Highlighter - extension extension link
let sd = [6,7,24,6,7,7,4,3,00]
sd.join("..") // OUTPUT: "6..7..24..6..7..7..4..3..0"
sd.join('yono') // OUTPUT: "6yono7yono24yono6yono7yono7yono4yono3yono0"
sd.join(' ') // OUTPUT: "6 7 24 6 7 7 4 3 0"
yui = sd.join(' ')
typeof yui //OUTPUT: "string"
sd.concat(999,999) // OUTPUT: (11) [6, 7, 24, 6, 7, 7, 4, 3, 0, 999, 999]
iuo = sd.concat(888,888)
typeof iuo // OUTPUT: "object"
<p id="demo">JavaScript can change HTML content.</p>
// ^^ this refers to the >> innerHTML property of the p tag(or any other tag).
<button type="button" onclick='document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Hello JavaScript!"'>Click Me!</button>
da-14.com - Trusted JavaScript Adepts - (Has Regular Blog)
React 16: A look inside an API-compatible rewrite of our frontend UI library - post@engineering.fb.com
JavaScript Examples Exercise JavaScript Type Conversion JavaScript and HTML DOM Reference
JavaScript Array prototype Constructor - Important Link to create external methods for Array.prototype.Ucase like methods , like this one was for changing every array element to uppercase.
Creating Snippets in Visual Studio Code
Distractions - JavaScript Array Iteration Methods , JavaScript Object Accessors , JavaScript Objects ,
Bored - LOok here -
tc39/proposal-object-rest-spread Destructuring assignment Spread syntax
W3schools.com - JavaScript Function Apply, JavaScript Function Call, JavaScript Use Strict,
Objects Some Concepts : source: Link
Object.assign() // creates shallow copy(1 level copy only, if objects are referenced in properties, this is useless)
Cloning Object:(Shallow Copy)
var obj = { a: 1 };
var copy = Object.assign({}, obj);
console.log(copy); // { a: 1 }
Deep Cloning an Object:(Deep Copy)
helpful link (question/answers) @ stackoverflow
helpfule link (amazing article)@ medium.com - this brings us to the conclusion of using rfdc(really fast deep clone) everytime so as to be protective from the negative effects of deep clone via the JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj)) method. i.e.,
“If you do not use Dates, functions, undefined, Infinity, [NaN], RegExps, Maps, Sets, Blobs, FileLists, ImageDatas, sparse Arrays, Typed Arrays or other complex types within your object, a very simple one liner to deep clone an object is: JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(object))” — Dan Dascalescu in his StackOverflow answer
Joni’s Recommendations of deep clone needs for redux states:-
Immer:- https://immerjs.github.io/immer/docs/introduction Quick Example from the above link:- immer at egghead.io - link read on medium about immer (haven’t read yet): - link immer at github - https://github.com/immerjs/immer immer at github.io - https://immerjs.github.io/immer/docs/introduction
import produce from "immer"
const baseState = [
{
todo: "Learn typescript",
done: true
},
{
todo: "Try immer",
done: false
}
]
const nextState = produce(baseState, draftState => {
draftState.push({todo: "Tweet about it"})
draftState[1].done = true
})
PREFFERED WAY TO DEEP COPY:- (rfdc has only 196 stars on github)
# best DEEP COPY
const clone = require('rfdc')() // Returns the deep copy function
clone({a: 37, b: {c: 3700}}) // {a: 37, b: {c: 3700}} // deep clones while preserving all the special data types discussed in above box.
# DEEP COPY
var obj1 = { a: 0 , b: { c: 0}};
let obj3 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj1));
let obj3
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj3)); // { a: 0, b: { c: 0}}
// This deep clone method has a side effect that some native objects would be converted to strings. for e.g., Date object will be converted to string, and further operations via the date methods cannot be implemented on them after that.
Shallow Copy VS. Deep Copy
function test() {
'use strict';
let obj1 = { a: 0 , b: { c: 0}};
let obj2 = Object.assign({}, obj1); // Creates shallow copy(1 level copy).
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj2)); // { a: 0, b: { c: 0}}
obj1.a = 1;
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj1)); // { a: 1, b: { c: 0}}
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj2)); // { a: 0, b: { c: 0}}
obj2.a = 2;
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj1)); // { a: 1, b: { c: 0}}
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj2)); // { a: 2, b: { c: 0}}
obj2.b.c = 3;
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj1)); // { a: 1, b: { c: 3}}
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj2)); // { a: 2, b: { c: 3}}
// Deep Clone
obj1 = { a: 0 , b: { c: 0}};
let obj3 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj1));
obj1.a = 4;
obj1.b.c = 4;
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj3)); // { a: 0, b: { c: 0}}
}
test();
Merging object:
var o1 = { a: 1 };
var o2 = { b: 2 };
var o3 = { c: 3 };
var obj = Object.assign(o1, o2, o3);
console.log(obj); // { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 }
console.log(o1); // { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 }, object "o1" itself is changed.
Merging objects with same properties:
var o1 = { a: 1, b: 1, c: 1 };
var o2 = { b: 2, c: 2 };
var o3 = { c: 3 };
var obj = Object.assign({}, o1, o2, o3);
console.log(obj); // { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 }
//o1,o2,o3 remains the same even though.
The properties are overwritten by other objects that have the same properties later in the parameters order.
https://github.com/tc39/proposal-object-rest-spread
Object Rest/Spread Properties for ECMAScript
ECMAScript 6 introduces rest elements for array destructuring assignment and spread elements for array literals.
This proposal introduces analogous rest properties for object destructuring assignment and spread properties for object literals. source: “Here the object spread syntax is being used, which hasn’t yet been standardized as a part of JavaScript’s language specification.” - Full Stack Course
Converting string to number with unary operator:
> y = "5"
<• "5"
> x = +y
<• 5
If the variable cannot be converted, it will still become a number, but with the value NaN
var y = "John"
var x = +y // x is a number NaN
PS:
> y = "5"
> q = 0+y
<•"05"
//Also
> Number("a")
<• NaN
//Also
> Number("10")
<• 10
//Also
> Number("10s")
<• NaN
//Also
> Number("true")
<• NaN
//Also
> Number(true)
<• 1
//Also
> Number(false)
<• 0
Use of JSON.stringify() and JSON.parse()
> w = {ram:20,shayam:40}
<• ►{ram: 20, shayam: 40}
> console.log(w+1)
<• [object Object]1
Arguments object for older Function -
> function yah(){ return(arguments.length)}
> yah(2,3,4)
<• 3
// with arrow function, throws error arguments is not defined.
> let yahu = () =>{ return(arguments.length)}
<• undefined
> yahu(2,3,5)
<• VM3640:1 Uncaught ReferenceError: arguments is not defined
at yahu (<anonymous>:1:20)
at <anonymous>:1:1
Also read here: - Passing an array as a function parameter in JavaScript
Answer:
const args = ['p0', 'p1', 'p2'];
call_me.apply(this, args);
or If the environment supports ECMAScript 6, you can use a spread argument instead:
call_me(...args);
> yahi = () => {return (arguments.length)}
<• () => {return (arguments.length)}
// if function is created with keyword "function", then it would be
> function yah(){ return(arguments.length)}
<• ƒ yah(){ return(arguments.length)}
> JSON.stringify(function radhe(){return 0}() )
<• "0"
> JSON.stringify(function radhe(){return 0} )
<• undefined // for all type of functions.
stackoverflow what is REQUEST PAYLOAD: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/23118249/whats-the-difference-between-request-payload-vs-form-data-as-seen-in-chrome
Add style to react using style attribute with dual curly braces.
<tr>
<td style=>{props.text}</td>
<td style=>{props.value}</td>
</tr>
Fix decimals in javascript : w3schools.com - Number.tofixed
Finding maximum value from the array:
console.log(Math.max(1, 3, 2));
// expected output: 3
console.log(Math.max(-1, -3, -2));
// expected output: -1
var array1 = [1, 3, 2];
console.log(Math.max(...array1));
// expected output: 3
Array.from() - w3schools - one of ECMA 6 Rules
Shallow Copy Only
Please note spread only goes one level deep when copying an array. So if you’re trying to copy a multi-dimensional arrays, you will have to use other alternatives.
source: ES6 Way to Clone an Array 🐑 look for more Star things.
Mutable vs Immutable Data Types
Mutable:
- object
- array
- function
Immutable:
All primitives are immutable.
- string
- number
- boolean
- null
- undefined
- symbol
Why Can’t I Use = to Copy an Array?
Because arrays in JS are reference values, so when you try to copy it using the = it will only copy the reference to the original array and not the value of the array. To create a real copy of an array, you need to copy over the value of the array under a new value variable. That way this new array does not reference to the old array address in memory.
const sheeps = ['🐑', '🐑', '🐑'];
const fakeSheeps = sheeps;
const cloneSheeps = [...sheeps];
console.log(sheeps === fakeSheeps);
// true --> it's pointing to the same memory space
console.log(sheeps === cloneSheeps);
// false --> it's pointing to a new memory space
Problem with Reference Values
If you ever dealt with Redux or any state management framework. You will know immutability is super important. Let me briefly explain. An immutable object is an object where the state can’t be modified after it is created. The problem with JavaScript is that arrays are mutable. So this can happen:
const sheeps = ['🐑', '🐑'];
const sheeps2 = sheeps;
sheeps2.push('🐺');
console.log(sheeps2);
// [ '🐑', '🐑', '🐺' ]
// Ahhh 😱 , our original sheeps have changed?!
console.log(sheeps);
// [ '🐑', '🐑', '🐺' ]
That’s why we need to clone an array:
const sheeps = ['🐑', '🐑'];
const sheeps2 = [...sheeps];
// Let's change our sheeps2 array
sheeps2.push('🐺');
console.log(sheeps2);
// [ '🐑', '🐑', '🐺' ]
// ✅ Yay, our original sheeps is not affected!
console.log(sheeps);
// [ '🐑', '🐑' ]
Shallow Copy Only
Please note spread only goes one level deep when copying an array. So if you’re trying to copy a multi-dimensional arrays, you will have to use other alternatives.
const nums = [
[1, 2],
[10],
];
const cloneNums = [...nums];
// Let's change the first item in the first nested item in our cloned array.
cloneNums[0][0] = '👻';
console.log(cloneNums);
// [ [ '👻', 2 ], [ 10 ], [ 300 ] ]
// NOOooo, the original is also affected
console.log(nums);
// [ [ '👻', 2 ], [ 10 ], [ 300 ] ]
🤓 Here’s an interesting thing I learned. Shallow copy means the first level is copied, deeper levels are referenced.
Community Input
Array.from is Another Way to Clone Array
const sheeps = ['🐑', '🐑', '🐑'];
const cloneSheeps = Array.from(sheeps);
Thanks: @hakankaraduman
-
@hakankaraduman: yes, I try not to use spread, it confuses me when reading the code because it does two things, spreading or gathering according to context
-
CJ J: I think the best way is the one that most closely matches the semantics of the operation. I prefer to use
Array.fromsource - same old one - www.samanthaming.com/
this resource - https://www.samanthaming.com/tidbits/35-es6-way-to-clone-an-array
antecdotes - https://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~damithch/pages/SE-quotes.htm
Index as a key is an anti-pattern@Medium MUST READ
https://reactjs.org/docs/lists-and-keys.html#keys
Js Refactor for easy conversion of arrow function to braces and vice versa
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/24427621/innertext-vs-innerhtml-vs-label-vs-text-vs-textcontent-vs-outertext/24428100
How TO - Filter/Search List with JS in w3schools.com - inspiration for making search engine
Providing ids to react JSX format - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38486660/how-to-add-a-classname-id-to-react-bootstrap-component
prettymuchsimilar
JS string slice - https://www.w3schools.com/jsref/jsref_slice_string.asp
Removing array elements in js - roughly need
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9289/removing-elements-with-array-map-in-javascript
//code for fetching persons form the data.json using axios, useState, and json-server// start any script with » npm run “script-as-defined-in-package.json–file” “”
// you may run react server via - npm run start OR npm start ; you may run json-server via npm run server (only if you have defined its loading config in scripts in package.json file properly.)
Using the effect hook - https://reactjs.org/docs/hooks-effect.html
There are two hooks - state hooks and effect hooks in react.
### effects in React:(useEffect)
import React, {useEffect} from ‘react’
or
import React, { useState, useEffect } from ‘react’
Data fetching, setting up a subscription, and manually changing the DOM in React components are all examples of side effects. Whether or not you’re used to calling these operations “side effects” (or just “effects”), you’ve likely performed them in your components before.
source: https://reactjs.org/docs/hooks-effect.html
suffice : be enough or adequate.
<input value={search} onChange={handleSearchChange} placeholder="Search.."></input>
Styling in react: Codeburst article, img tag in react ,styling in react @w3schools.com,
learn methods - Javascript https://www.w3schools.com/jsref/jsref_filter.asp
Jquery searching(although I didn’t used it.) - https://www.w3schools.com/jquery/jquery_filters.asp
Learning Jquery - https://www.w3schools.com/jquery/
Read about promises in JS - @MDN @suggested by fullstack course
code becomes bloated:
swollen and rounded because of containing too much air, liquid, or food:
Running json-server locally(meaning to be able to access via 192.168.43.29 via mobile) via npx command in the node package-
•To run at local address i.e. 192.168.43.29 on default port 3000 via npx for locally instlled on default port
npx json-server --host 192.168.43.29 db.json
•Common custom is to run the json-server on port: 3001 via below command:
npx json-server --host 192.168.43.29 --port 3001 db.json
•Command on Fullstackopen.com -
json-server -p3001 db.json
src: @StackOverflow
npm vs. npx
src: @StackOverflow
Serve multiple files via npm -
typicode commented on Apr 25, 2016 - I can see another ways of doing this, but it has cons.
Create db.js:
module.exports = function() {
return {
one: require('./one.json'),
two: require('./two.json')
}
}
run the json-server via -
json-server db.js
See all the objects in the two json files at http://localhost:3000/db (no matter how many files you join the db.js file or may be SomeTHingName.js , the database will always be available @ URL localhost:3000/db -the complete database including multiple files ) Also, the database can also be fetched via the imported varible names i.e., localhost:3000/one or localhost:3000/two individually.
Data won’t be persisted and you can’t watch for changes. But if it’s a test, that’s fine.**
**Or, as suggested previously, manually copy the content of the JSON files and create a db.json file. Unlike the db.js solution, If you restart your server, changed data won’t be lost.
If you are working with routes like above and want to be working with resource like -
localhost:30001/ persons, then you may server the file as array of object(not the object which contains the resource (property) i.e. persons).
Earlier, while serving the data.json was containing an object which contained a property naming persons which further contains an array of objects.
And, now we have defined the array of objects itself in the route file and imported it as variable persons in the TheSingleFileWorkedAsIs.js otherwise - server.js (actually linked to db.js which contains the persons route)
src: @StackOverflow(two-files-js) src: github.com/tpicode
Referring comments in json - @StackOverflow
export default {getAll,create,update}
// export default {
// getAll: getAll,
// create: create,
// update: update
// }
***
import axios from 'axios'
import Note from './components/Note'
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
import noteService from './services/notes'
import React, { useState } from 'react'
How to make HTTP requests like a pro with Axios
VSCODE MASTERY-
Ctrl+shift+. => Navigate Through the code via the OUTLINE(also present in left panel)
Ctrl+. => Code Actions
Ctrl+, => Settings
Ctrl+L => Select the whole current line and then selects the line below it if further pressed.
Alt+right or Alt+left for adjusting the window to the left or right according to the use in VS code.
Ctrl+e => Open the easy files navigator
Ctrl+shift+L => selects the selected text everywhere and places cursor there too. AWESEO
IMPORTING CSS FILE IN REACT -
import './index.css'
Centering the content of div elements in html (or React)
<div align="center" style={footerStyle}>
Pseudo-classes @ MDN Web Docs DOM Elements @ React Docs
npm/validate-npm-package-name - Good list of rules defining the name.
How open source licenses work and how to add them to your projects
Ctrl+shift+m in chrome » shows the user in chrome and tripple tab for passwords field>Enter.
Chrome: @StackOverflow - transferred vs. resources
In node use backslash for any characters like ‘ in strings there for escaping characters.
Load time vs. Finish time. Finish time: Includes the asynchronously loading(non blocking) objects/elements on the page which may continue downloading way after the onload event for page has fired.
Load time: Response time for a website generally speaking means ‘Load’ time because that is more easily user perceivable, at this point user can see browser has finished working and page is ready on their screen. Finish time, although technically also a response time doesn’t have as much end-user implication.
In some cases it seems the Finish timer never stops and continues increasing so it may not be the best assessment of web page response time.
Idempotence means that applying an operation once or applying it multiple times has the same effect.
The next step is to add the library Morgan. Install it by running npm install morgan. We’ll need Morgan to know of the request id we added to the request body in the last step. So in the file app.js.
Non-existent Files - https://superuser.com/questions/1060888/non-existent-files-in-windows-documents-folder
Download a file with Curl: (usually github)
curl -LO https://github.com/github/gitignore/raw/master/Node.gitignore
//here -L option provide the service of redirection.
//here -O(uppercase) options tells curl to save with name of original file
//here if there would be lowercase o, then we woud provide the filename additionally with the desired extension.
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/github/gitignore/master/Node.gitignore
Below command doesn't work-
curl -LO https://github.com/github/gitignore/blob/master/Node.gitignore
•rm -rf x
x - Could be a single file/folder.
•rm -rf .
. means everything in the current folder except hidden files/folder(i.e files/folders starting with .)
• rm -rf .*
.* means everything in the current folder.
Removing a git could be done as ..
• rm -rf .git
this would simply delete the .git folder in current folder.
Network Analysis Reference - Chrome
Blogpost @ developers.google.com
var text = '3.14someRandomStuff234';
var pointNum = parseFloat(text);
// returns 3.14 // returns only the digits with decimal till letter character is encountered.
var text = '42px';
var integer = parseInt(text, 10);
// returns 42 // returns without any decimal
"I am number 1 and I love number 13.".replace(/[^0-9]/g,'')
// output => "113"
"Anything that is some string.".replace(/[^a-zA-Z0-9]/g,'-');
// outpu => it wud output the string only with the character set defined above i.e., a to z ; A to Z; and 0 to 9. If it found any other character then it would replace it with character '-'.
src : Link to StackOverflow question.
By adding our .cleanup() method to the String object itself, you can then cleanup any string in Javascript simply by calling a local method, like this:
# Attaching our method to the String Object
String.prototype.cleanup = function() {
return this.toLowerCase().replace(/[^a-zA-Z0-9]+/g, "-");
}
# Using our new .cleanup() method
var clean = "Hello World".cleanup(); // "hello-world"
Because there is a plus sign at the end of the regular expression it matches one or more characters. Thus, the output will always have one '-' for each series of one or more non-alphanumeric characters:
# An example to demonstrate the effect of the plus sign in the regular expression above
var foo = " Hello World . . . ".cleanup(); // "-hello-world-"
Without the plus sign the result would be "--hello-world--------------" for the last example
w3school - replace()jsref/jsref_replace.asp
JavaScript toJSON() Method: Definition and Usage
The toJSON() method converts a Date object into a string, formatted as a JSON date.
JSON dates have the same format as the ISO-8601 standard: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.sssZ
| Return Value: | A String, representing the date and time formated as a JSON date |
|---|---|
| JavaScript Version: | ECMAScript 5 |
throw keyword:
You may throw CUSTOM ERRORS like the one below:
try {
if(true) throw "Too big";
}
catch (err) {
console.log('Error is:',err,'\nWith err.message:',err.message)
}
//Output:
Error is: Too big
With err.message: undefined
**
Different style of throw:
All below thrown values will cause the program to abrubt and show what is thrown….
throw { name: "Nicholas" };
// Uncaught {name: "Nicholas"}
throw true;
// Uncaught true
throw 12345;
// Uncaught 12345
throw new Date();
// Uncaught Sun Apr 19 2020 18:28:04 GMT+0530 (India Standard Time)
throw "message";
// Uncaught message
throw new Error("*****Whooooooooooooops!********");
// throw error
**
Create your own custom error:
Read this amazing article on medium, to find out more about logging errors in a good way. Link
function MyError(message){
this.message = message; //you may specify more things here....according to need...
}
throw new MyError("Hello world!");
//Output: Uncaught MyError {message: "Hello world!"}
Try and catch error in JS
Note.findById(request.params.id)
.then(note => {
// console.log("---sf-sf---s-ff-befor .. note.JSON()");
response.json(note.toJSON())
throw new Error("*****Whooooooooooooops!********");
})
.catch(err => console.log(err))
// Output: Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected token '=>'
*********************************************************************
Syntax of try and catch :
try {
Block of code to try
}
catch(err) {
Block of code to handle errors
}
************************************************************************
Optionally you can use finally too:
try {
Block of code to try
}
catch(err) {
Block of code to handle errors
}
finally {
Block of code to be executed regardless of the try ''/ catch result
}
***********************************************************************
NOTE: For .then PROMISES YOU have to use callback for the catch...like below
.then((val)=>consolle.log(val, "error bcoz consolle is not correct")).catch(err => console.log('pippi is throwing error, my lord. err:',err) )
Rest Client - Read here knowledge spreads..
Api - https://swapi.co
Clean unused dependenices in package.json
npm cache clean
npm ERR! As of npm@5, the npm cache self-heals from corruption issues and data extracted from the cache is guaranteed to be valid. If you want to make sure everything is consistent, use 'npm cache verify' instead. On the other hand, if you're debugging an issue with the installer, you can use `npm install --cache /tmp/empty-cache` to use a temporary cache instead
of nuking the actual one.
npm ERR!
npm ERR! If you're sure you want to delete the entire cache,
rerun this command with --force.
npm ERR! A complete log of this run can be found in:
npm ERR! C:\Users\chetan\AppData\Roaming\npm-cache\_logs\2019-11-07T03_08_56_989Z-debug.log
//So hereby use if you want to force npm to clean ca
npm cache clean --force
npm cache verify
***
$ npm -v
// Output: 6.9.0
$ npm install -g npm
$ npm -v
// Output:6.14.4
npm - using stale package data - Error??
rm ./package-lock.json
rm -r ./node_modules
npm cache clear --force
//Javascript replace method to retain only character from numeric 0 to 9.
ii = ii.replace(/[^0-9]/g,'')
Minimum and maximum value for a number in personSchema in moongose.Schema
Mongoose Schema number field to be at exact length
rules: {"no-unused-vars": "off"}
For disabling the error for unused variables - eslint.
You should always use lines as ‘unix’ in eslint,(.eslintrc.js file).
Minimise Everything with [Winodws + M]
command prompt:
if 2 EQU (ECHO "Amazing thing") else (echo "Not such amazing thing")
if not exist "C:\VTS\" mkdir C:\VTS
Connect to adb over wifi:
connect mobile with usb to pc
And make sure you have it in the devices: adb devices
Then make the listen on other port
adb tcip 5555
Disconnect the device.
Connect to device over wifi
{you can use arp -a command to scan the connected devices with the network you have connected to (you may confirm with the mac accress.)}
adb connect
Store a file:
Press win+X and press a (To open command prompt as admin.)
Execute the below code in once.
cd /adbPulledData
adb connect 192.168.43.1:5555
adb pull /sdcard/Apple/Mahabharat/51-71/new/76(240P).mp4 ./
adb pull /sdcard/Apple/Mahabharat/51-71/new/77(240P).mp4 ./
adb pull /sdcard/Apple/Mahabharat/51-71/new/78(240P).mp4 ./
adb pull /sdcard/Apple/Mahabharat/51-71/new/79(240P).mp4 ./
adb pull /sdcard/Apple/Mahabharat/51-71/new/80(240P).mp4 ./
adb pull /sdcard/Apple/Mahabharat/51-71/72.mp4 ./
#THIS LINE IS INTENTIONALLY PUT. To let the last command execute(with the newline character).
adb pull /sdcard/Apple/Mahabharat/www ./
#Above command will pull the complete folder www to the current folder.
adb push <file/folder to be pushed> /sdcard/Apple
# To Disconnect all devices:
adb disconnect
async await, promises
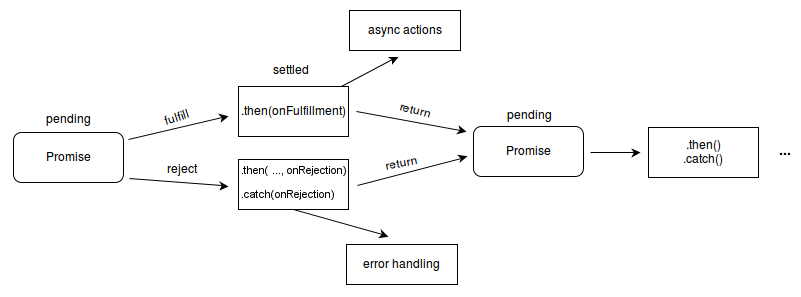
https://medium.com/better-programming/should-i-use-promises-or-async-await-126ab5c98789
Why Is Export Default Const invalid in node(react style)?
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/36261225/why-is-export-default-const-invalid
React Hooks: How to use useEffect() @medium.com
https://medium.com/javascript-in-plain-english/react-hooks-how-to-use-useeffect-ecea3e90d84f
follow the related code in your code in the help code folder. yeah…!!
useEffect(() => {
user && blogService.getAll().then((initialNotes) => setBlogs(initialNotes));
console.log("useeffect executed..");
});
//here above code can only access the user variable from the the app component if it is set to update on every render
***
# below code is suggested by hook-guide in chrome dev tools**
useEffect(() => {
user && readyToFetch&& blogService.getAll().then((initialNotes) => setBlogs(initialNotes)) && setreadyToFetch(false)
console.log("useeffect executed..");
},[user,readyToFetch]);
///the last parameter i.e., [user, readyTOFetch] states that only when these variables have changes then only the useEffect() function will execute.
Master the JavaScript Interview: What is a Promise? @medium.com « IMPORTANT AS HELLLL.
https://medium.com/javascript-scene/master-the-javascript-interview-what-is-a-promise-27fc71e77261
.then(func1,func2)
func1 will execute if promise is fulfilled, and func2 will execute if promise if rejected.
Promises
//everything returned from a .then method is a promise.
//to fetch the array of data from it, you need to assign from inside it
// like .then(t=>variable=t) and variable will be assigned the data from the promise.